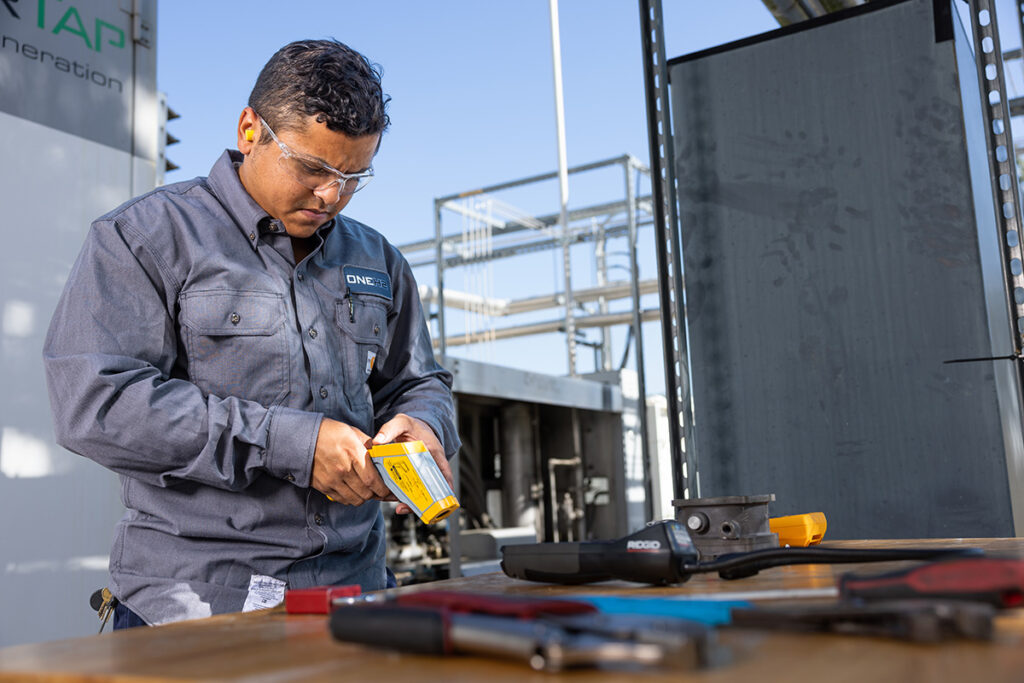
From generation to consumption, we incorporate industry safety standards into every step of our hydrogen fueling systems. The health and safety of our team, our clients, the community, our stakeholders and the environment are of utmost importance to us. We know that making hydrogen fuel a viable clean energy solution means ensuring safe generation, transportation, and utilization processes.
With any fuel source, proper safety protocols must be followed. When safe handling procedures are adhered to, hydrogen is less dangerous than gasoline and other conventional fuels. Hydrogen’s safety advantages include:
Unlike gasoline and other fossil fuels, hydrogen is non-toxic and will not contaminate the environment or harm human health in the event of a leak.
Hydrogen is lighter than air, which allows it to disperse quickly in the event of a leak, reducing the risk of fire or explosion.
Hydrogen has a lower radiant heat than gasoline, which means the air around a hydrogen flame is less hot than around a gasoline flame. This means hydrogen has less risk of secondary fires.
Hydrogen requires a higher oxygen content to ignite, making it safer in environments with oxygen.
Multiple organizations have come together to develop robust safety standards for hydrogen systems and fuel cells. These organizations include; the US Department of Energy, International Code Council, and the National Fire Protection Association.
Safety standards for hydrogen encompass all aspects of the hydrogen fuel lifecycle – from generation to utilization. These include:
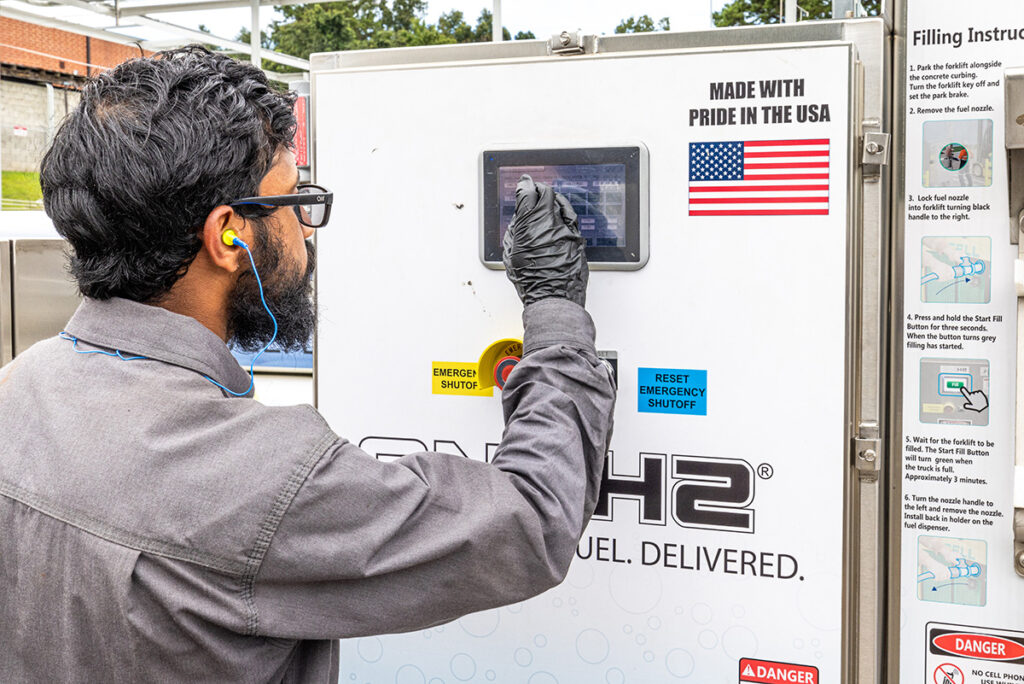

Hydrogen must be stored in containers specifically designed for this gas and kept in well-ventilated areas away from heat, sparks, and flames.
Hydrogen must only be transported in tanks and vehicles equipped with safety features such as pressure relief valves and explosion-proof construction.
Hydrogen fuel systems must be equipped with leak detection devices to quickly detect and respond to any leaks.
Fueling hydrogen vehicles should only be done in well-ventilated areas, following the manufacturer's recommended procedures.
Individuals who work with hydrogen fuel must receive proper training and education on its safe handling and use, including emergency response procedures.
Hydrogen fuel systems must be regularly maintained to ensure they're functioning properly and to identify any potential safety hazards.
OneH2 closely follows all hydrogen fuel safety standards. When compared to conventional fuels such as gasoline, hydrogen is a safer and more sustainable alternative. With the proper safety procedures in place, hydrogen fuel is a safe and reliable fuel source.